简介
JS 应用的状态容器,提供可预测的状态管理
三大原则
1、单一数据源
整个应用的全局 state 被存储在一棵 object tree 中,并且这个 object tree 只存在于唯一一个 store 中
2、state是只读的
唯一改变 state 的方法就是触发 action, action 是一个用于描述已发生事件的普通对象。
3、使用纯函数来执行修改
为了描述 action 如何改变 state tree,你需要编写纯的 reducers。
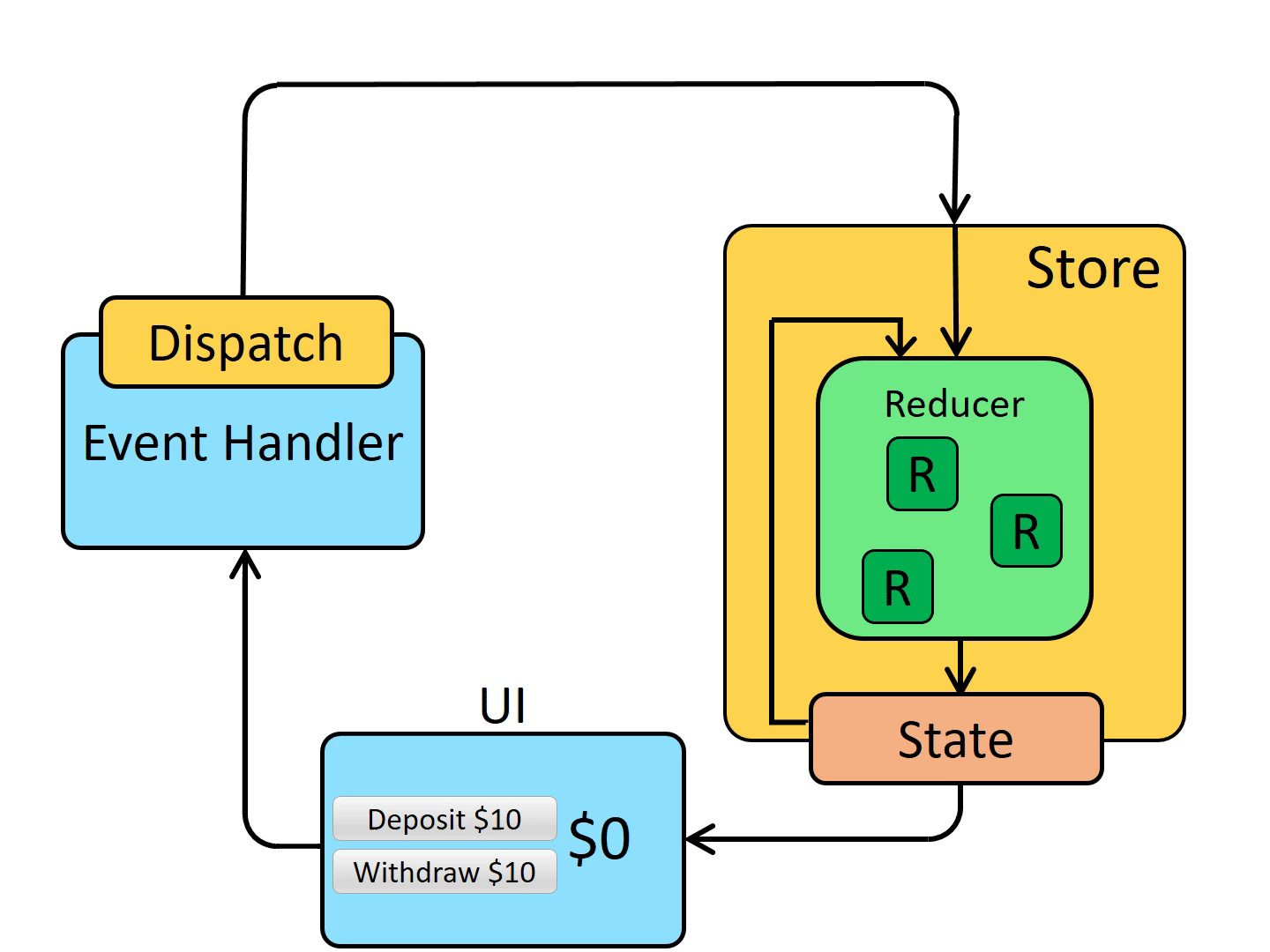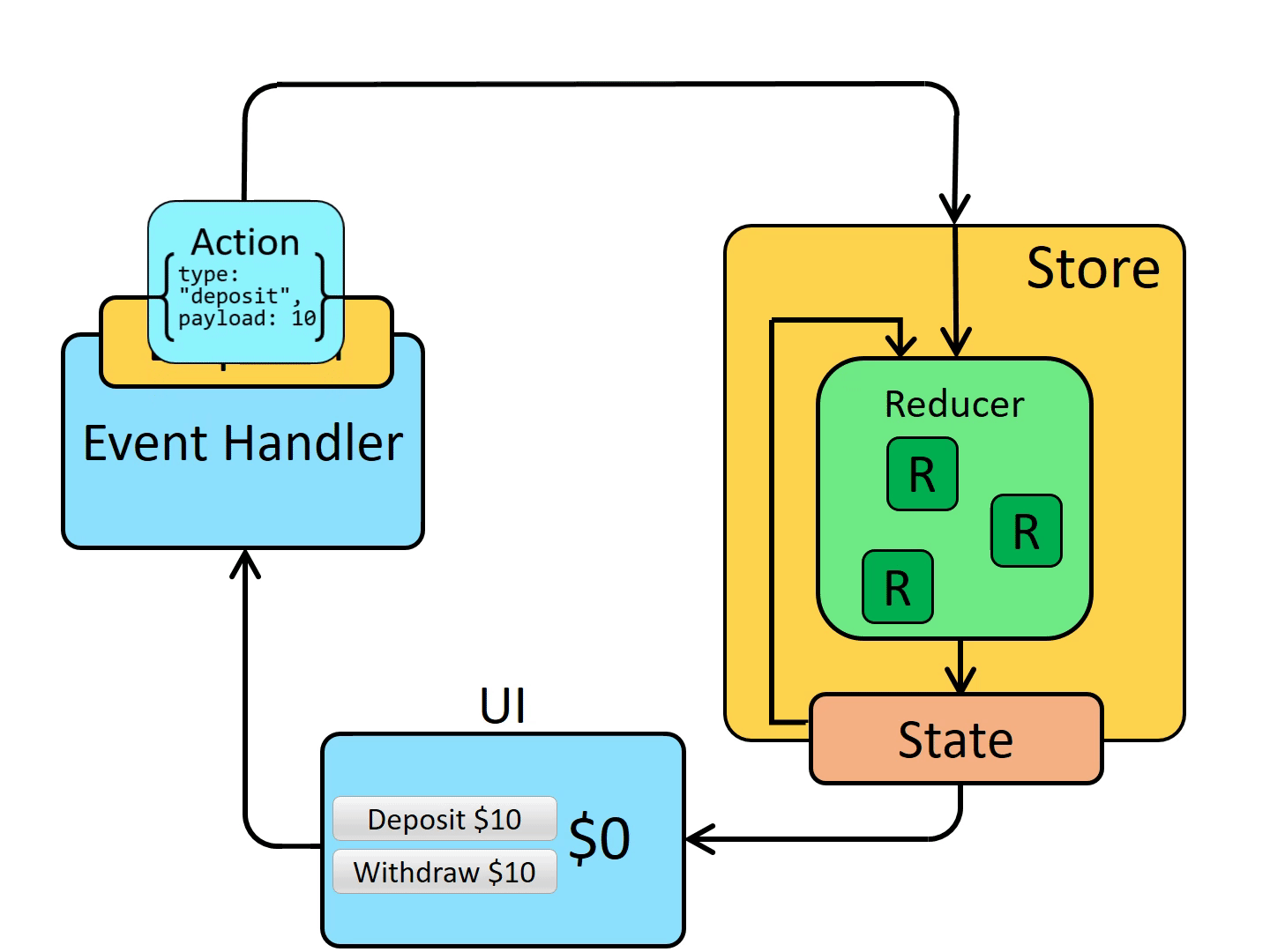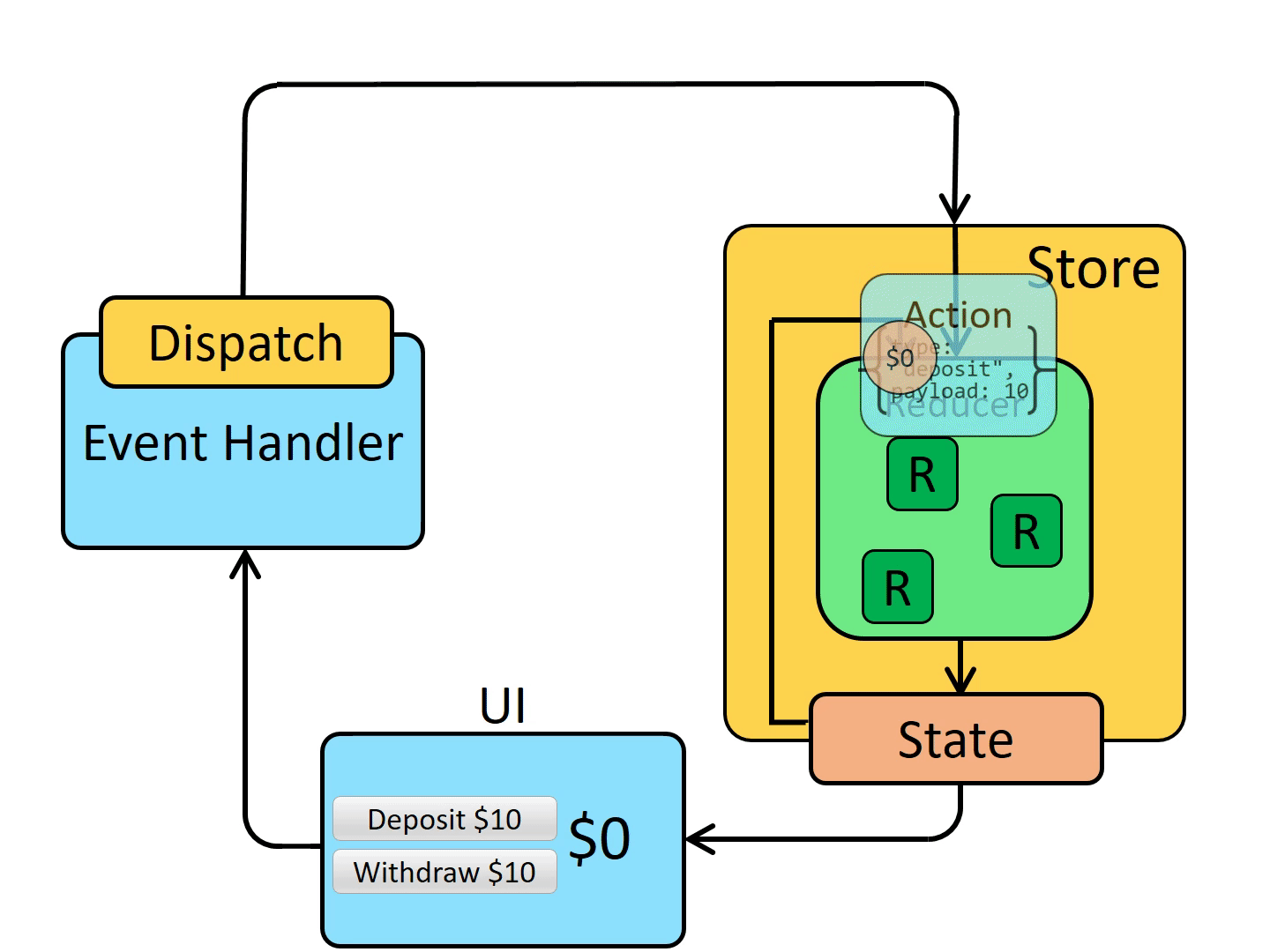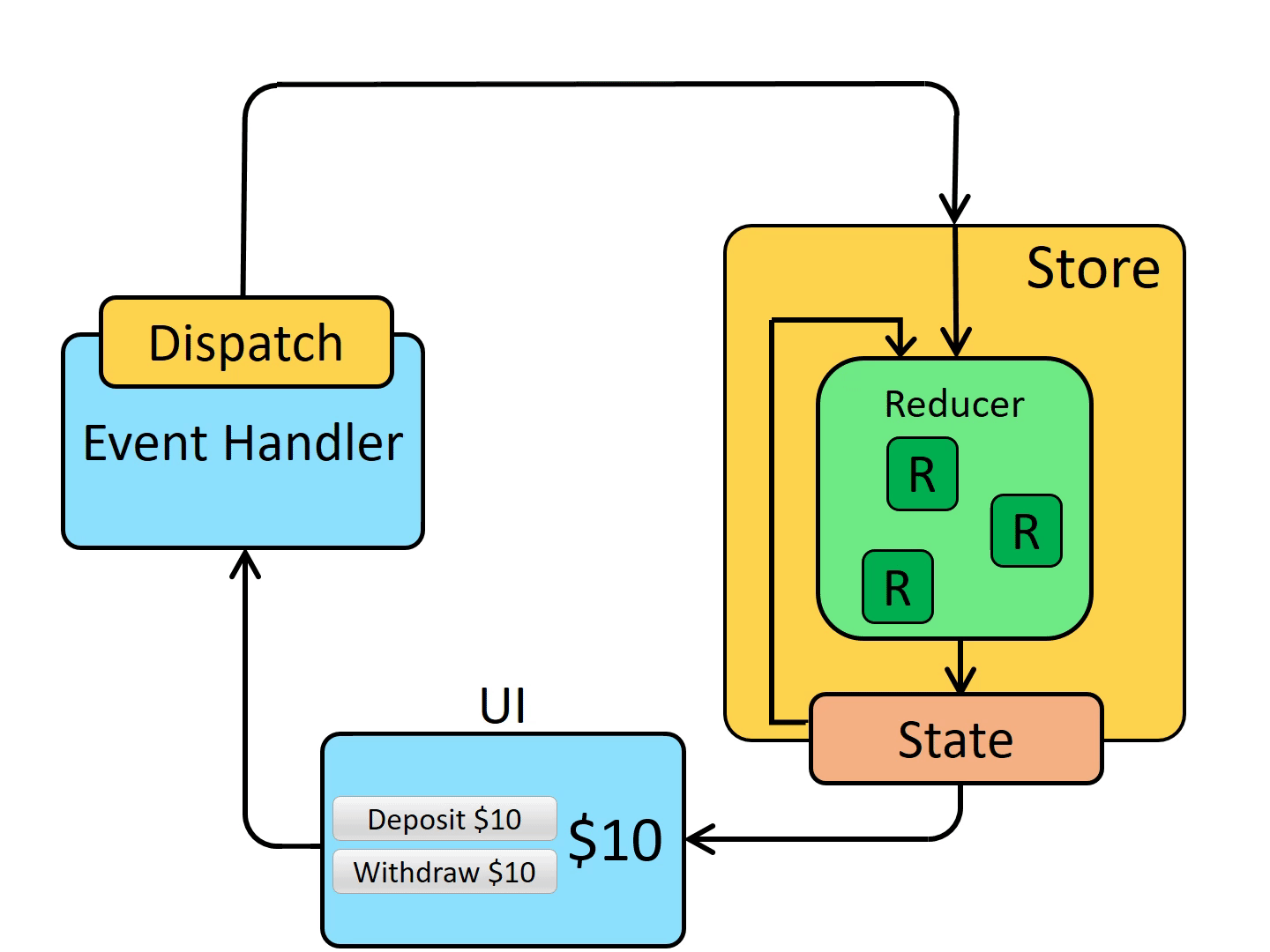
单向数据流
1
| view -> dispath(action) -> reducer -> subscribe -> view(流回)
|
流程
同步
同步的 redux 可以非常清晰的体现出 3 大原则和单向数据流。
异步
redux 本身不提供处理异步的方式,如果你需要异步的操作需求,可以添加 middleware 来增强 redux 的功能。
核心
顶级API
1、createStore(reducer, [preloadedState], [enhancer])
创建store接收三个参数:
- reducer 是一个函数,返回新的状态,接受两个参数:当前的 state 和要触发的 action ;
- preloadedState 为初始时的 state 对象;
- enhancer 可选使用。用第三方第能力如中间件、时间旅行、持久化来增强 store;
2、combineReducers(reducers)
合并 reducer 单元,返回combination(state, action),即 reducer。
3、applyMiddleware(…middlewares)
扩展中间件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import compose from './compose'
export default function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
return (createStore) => (...args) => {
const store = createStore(...args)
let dispatch = () => {
throw new Error(
'Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ' +
'Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.'
)
}
const middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (...args) => dispatch(...args),
}
const chain = middlewares.map((middleware) => middleware(middlewareAPI))
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch,
}
}
}
|
4、 bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch)
包装
5、compose(…functions)
组合函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| export default function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return (arg) => arg
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce((a, b) => (...args) => a(b(...args)))
}
|
Store API
- getState
- dispath
- subscribe
- replaceReducer
当 enhancer 传参的时候
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
if (typeof enhancer !== 'function') {
throw new Error(
`Expected the enhancer to be a function. Instead, received: '${kindOf(
enhancer
)}'`
)
}
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
}
|
getState
返回应用当前的 state 树
1
2
3
| function getState() {
return currentState
}
|
dispath
分发 action。这是触发 state 变化的惟一途径。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| function dispatch(action) {
...
try {
isDispatching = true
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
const listener = listeners[i]
listener()
}
return action
}
|
subscribe
添加一个变化监听器。每当 dispatch action 的时候就会执行,state 树中的一部分可能已经变化。你可以在回调函数里调用 getState() 来拿到当前 state。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| function subscribe(listener) {
...
var isSubscribed = true
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
nextListeners.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed) {
return
}
isSubscribed = false
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
var index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener)
nextListeners.splice(index, 1)
}
}
|
replaceReducer
替换 store 当前用来计算 state 的 reducer。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| function replaceReducer(nextReducer) {
if (typeof nextReducer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Expected the nextReducer to be a function.')
}
currentReducer = nextReducer
dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.INIT })
}
|
扩展
我们知道将 reducer 设计为纯函数,让它们更容易调试和比较;但这也带来了其它问题,比如涉及到接口调用之类的就不能处理。那么中间件便是用来增强 redux 功能的一种中间函数。
以 Redux-thunk 为例,以下为 thunk 的实现源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function createThunkMiddleware(extraArgument) {
return ({ dispatch, getState }) =>
next =>
action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument);
}
return next(action);
};
}
|
生态库
- Redux Toolkit
- Redux-thunk
- React-redux
- React-redux-router
参考
Redux 中文官网

